Your guide to Lignin and Lignosulfonates
Lignin is the binding agent in wood and the world’s second most abundant biopolymer after cellulose. Lignin is the raw material for Borregaard's range of sustainable lignosulfonate products.
Table of contents
- 1. What is lignin?
- 2. What is the function of lignin in plants?
- 3. What are the different types of lignin products?
- 4. What are lignosulfonates and how are they produced?
- 5. What are the functional properties of lignosulfonates?
- 6. In what industrial applications can lignosulfonates be used?
- 7. What types of lignosulfonates are available commercially?
- 8. What are the environmental benefits of using lignosulfonates?
- 9. How is the sustainability of lignosulfonates documented?
1. What is lignin?
The main function of lignin in plants is binding the fibres together, imparting structural rigidity and creating a composite material that is outstandingly resistant to impact, compression and bending. Lignin is a complex organic polymer that is an important component of the cell walls of many plants. It is found in the secondary cell walls of most vascular plants, where it provides strength and rigidity to the plant tissue.
Lignin is a highly cross-linked polymer made up of aromatic compounds, primarily phenylpropanoids. It is highly hydrophobic, making it resistant to degradation by microorganisms, and contributes to the structural integrity of plant cell walls.
Lignin is found in a wide variety of plant tissues, including woody stems, bark, roots and some seeds. It is also present in some algae and certain types of bacteria. In the pulp and paper industry, lignin is an important product that can be extracted and used for a variety of industrial purposes.
2. What is the function of lignin in plants?
The primary function of lignin in plants is to provide structural support to the cell walls of plant tissues. Lignin works in conjunction with other components of the cell wall, such as cellulose and hemicellulose, to create a strong, complex structure that allows the plant to grow and maintain its shape.
Lignin also plays a role in water transport within plants. In some plants, lignin forms a network of tubes that help transport water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant. This is especially important in woody plants, which require a strong and efficient water transport system to support their growth and survival.
In addition to its structural and transport functions, lignin provides protection against pests and pathogens. Lignin can also help plants cope with environmental stress such as drought or extreme temperatures by providing additional support and stability to plant tissues.

3. What are the different types of lignin products?
The three most common manufacturing processes of lignin when utilising wood as raw material are sulfite, kraft and organosolv pulping. The different processes result in different types of lignin products. The properties of these lignins can vary depending on their raw material source, pulping process, and purification and modification methods. For example, sulfite lignin, or lignosulfonate, produced in the sulfite pulping process can be used as a speciality chemical for a wide range of industrial applications. Kraft lignin is a by-product of the kraft pulping process and is typically burned to recover energy and chemicals. Organosolv lignin is produced by extraction with organic solvents.
Borregaard is the world's leading producer and supplier of lignosulfonates.
4. What are lignosulfonates and how are they produced?
Lignosulfonates are water-soluble, sulfonated derivatives of lignin that are produced during the sulfite pulping process of wood. The sulfonation process introduces sulfonic acid groups onto the lignin structure, resulting in a water-soluble polymer that can be used for various industrial applications.
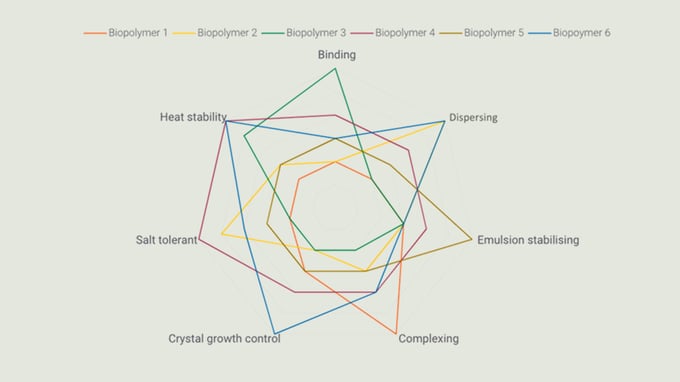
Figure: Properties of Borregaard’s lignosulfonates
Native properties of lignin, in combination with customised modification, have resulted in production of a wide portfolio of sustainable lignosulfonates, which are used in a variety of applications, including dispersing, binding, crystal growth control, complexing, and emulsion-stabilising, among others.
5. What are the functional properties of lignosulfonates?
Lignosulfonates are versatile, water-soluble polymers that can provide various functionalities depending on their molecular weight, degree of sulfonation, amphiphilicity, purity and other factors. These biopolymers are particularly useful as:
- dispersants
- binding agents
- crystal growth modifiers
- emulsion stabilisers
- complexing and chelating agents
In fact, their multifunctional properties make lignosulfonates ideal for a broad range of industrial applications (see point 6 below).
Lignosulfonates are also biodegradable1, non-toxic and renewable, making them a sustainable alternative to synthetic polymers.
6. In what industrial applications can lignosulfonates be used?
Lignosulfonates have widespread use as dispersants, binders, crystal growth modifiers, emulsion stabilisers and complexing agents. Due to being water soluble, lignosulfonates find primary application in water-based industrial applications, including (but not limited to):
Agriculture
Lignosulfonates can be used as sustainable functional ingredients for plant nutrition and as co-formulants, ingredients and adjuvants for crop protection. The products can also be used as binders for seed coating to improve strength and handling.
Animal feed
Lignosulfonates are commonly used as binding agents in animal feed production to enhance pellet quality and minimise the formation of dust fines throughout feed processing, handling and storage.
Batteries
In lead acid batteries, lignosulfonates can be used as organic expanders to significantly improve charge acceptance, cold crank and cycle life. In lithium-ion batteries, they can be used as dispersants for viscosity control in the electrode slurry.
Biomass pelleting
Lignosulfonates can be used as bio-based binding agents in the production of biomass pellets, improving their durability, density and manufacturing efficiency.
Carbon black
Lignosulfonates can be used as binding agents for pelleting and granulation of both virgin and recovered carbon black, improving their handling and storage while reducing dust emissions. Lignosulfonates can also be used as dispersants for pigments, including carbon black. See ‘Pigments’ below.
Ceramics
Lignosulfonates can be used as sustainable binders and dispersing agents in the production of ceramics and refractory products.
Coal gasification
Lignosulfonates can be used as dispersants in coal gasification, improving the handling and flowability of coal particles.
Concrete and mortar
Lignosulfonates can be used as efficient water-reducing agents in concrete and mortars, improving their workability, strength, and durability as well as improving the sustainability of the construction industry.
Dust control
Lignosulfonates can be used as environmentally friendly dust suppressants in applications such as gravel roads, mining roads, bike trails, agriculture, stockpiles etc., by binding fine particles together and reducing the dust generated.
Emulsions
Lignosulfonates can be used as sustainable and effective emulsion stabilisers in various industries, such as paint, coating, and textile, improving the stability, uniformity, and viscosity of the emulsions.
Gypsum board
Lignosulfonates can be used as sustainable dispersants and binders in gypsum board production, improving the flowability, workability, and strength of the slurry.
Industrial binders (Agglomeration)
Lignosulfonates can be used as cost-effective binding agents in the agglomeration of raw materials and process fines, improving their storage and handling, while reducing dust emissions and improving the product's mechanical properties.
Leather tanning
Lignosulfonates can be used as dispersants and tanning agents in the leather industry, improving the penetration and uniformity of dyes and tanning agents while also reducing the environmental impact of the process.
Oil well drilling
Lignosulfonates are used as fluid loss control agents and as dispersants in oil drilling fluids to improve their stability and reduce the risk of formation damage.
Papersizing
Lignosulfonates can be used as sustainable and cost-effective sizing agents in papermaking to improve the drainage and retention of fibres, reduce the use of chemical additives, and enhance the strength of the paper.
Pigments
Lignosulfonates can be used as dispersants or milling aids for organic and inorganic pigments in various industries such as rubber, printing inks and paint, improving their dispersion and stability in the final product.
Resins and adhesives
Lignosulfonates can be used as extenders or to partially replace phenol in the production of resins and adhesives, improving the sustainability profile.
Road stabilisation
Lignosulfonates can be used as cost-effective, sustainable and environmentally friendly binders for road stabilisation and full-depth reclamation (FDR).
Textile dyestuffs
Lignosulfonates are used as sustainable dispersants in textile dyeing and printing to increase milling efficiency and solids loading in water-based systems.
Water treatment
Lignosulfonates can be used as bio-based flocculants in water treatment, facilitating the removal of suspended solids and organic matter from wastewater and improving its quality.
These are just a few examples of the many industrial applications of lignosulfonates.
Contact us if you want to discuss an application that is not covered here!
7. What types of lignosulfonates are available commercially?
There are various types of lignosulfonates available commercially, such as calcium, sodium, ammonium and magnesium lignosulfonates, among others. It is important to note that different manufacturers may offer a range of lignosulfonate products with different properties and applications depending on the manufacturing process and intended use.
Lignosulfonates are typically sold either as powder or liquid, making them easy to handle and store.
By selecting the appropriate type of lignosulfonate for a given application, manufacturers can enhance the performance and efficiency of their products while minimising costs and environmental impact.

8. What are the environmental benefits of using lignosulfonates?
Lignosulfonates are renewable, biodegradable1 and non-toxic, making them a sustainable alternative to synthetic polymers in many industrial applications. They also have a lower carbon footprint than fossil-based chemicals, as they are derived from a natural source and require less energy to produce.

9. How is the sustainability of lignosulfonates documented?
The environmental impact of lignosulfonates is documented through life cycle assessments (LCAs). Life cycle assessments can be used to compare the environmental impact of different materials over their life cycle. Several LCA comparisons done by company NORSUS have shown that lignosulfonates have a lower environmental impact than synthetic polymers, in terms of greenhouse gas emissions, energy use and other factors.
Additionally, LCA data can be used to create Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) for lignosulfonates. EPDs are standardised documents that provide verified, transparent and comparable information on the environmental performance of a product or service throughout its life cycle.
Learn more about sustainability documentation for Borregaard's lignin-based products →
Examples of LCA comparisons with Borregaard's products vs alternatives:
Marasperse AG vs EDTA (plant nutrition)
Dustex vs salts (dust suppression)
SoftAcid vs formic acid (animal feed acidification)
.png?width=517&height=128&name=Group%20(2).png)